Harlan 动脉粥样硬化(胆固醇、脂肪、胆酸盐) 饲料Atherogenic
Harlan Teklad动物饲料
Harlan代理
欢迎新老客户访问Harlan官网或者咨询中国代理商上海金畔生物获取更多详细资料。
Harlan 动脉粥样硬化(胆固醇、脂肪、胆酸盐) 饲料Atherogenic
Atherogenic
| Research use | Key dietary features | Examples |
| “Western” purified atherogenic diet | ||
| Accelerated hypercholesterolemia and plaque formation in genetically modified models such as Apoe and Ldlr deficient mice. Used for diet induced obesity in a variety of rodent models. |
High fat diet (20 – 23% by weight; 40 – 45% kcal from fat) Saturated fatty acids (SFA >60% of total fatty acids) Milkfat/butterfat Sucrose (34% by weight) Cholesterol (0.2% total) |
TD.88137 TD.10885 |
| “Western” purified atherogenic diet with added cholesterol and cholate source* | ||
| Induce hypercholesterolemia and mild atherosclerosis (foam cells, fatty streaks) in primarily wild type mice and rats. Will not promote obesity. |
High fat diet (15 – 20% by weight; 34 – 45% kcal from fat) Saturated fatty acids (SFA >55% of total fatty acids) Milkfat/butterfat, cocoa butter Sucrose (30-50% by weight) Cholesterol (1 – 1.25%) Cholate Source (0.5%)* |
TD.02028 TD.09237 |
| Hybrid high fat diets with added cholesterol and cholate source* | ||
| Induce hypercholesterolemia and mild atherosclerosis (foam cells, fatty streaks) in primarily wild type mice and rats. Will not promote obesity. Also used for lithogenic (gallstone) rodent studies. |
75% rodent breeder diet; 25% purified ingredients High fat (~15% by weight; 37% kcal from fat) Saturated fatty acids (SFA >45% of total fatty acids) Cholesterol (1.25%) Cholate source (0.5%)* |
TD.88051 TD.90221 |
| Standard diets with added cholesterol | ||
| Induce hypercholesterolemia in genetically modified and wild type models without promoting obesity. | Standard, grain-based rodent diet Minimal/moderate phytoestrogen diets recommended Cholesterol (1 – 4%) |
TD.120097 TD.07841 TD.01383 |
*Sodium cholate or cholic acid aid cholesterol and fat absorption and reduce cholesterol disposal via bile acid synthesis. However, if including a cholate source is not desired for your research, diets without cholate are available.
*Sodium cholate or cholic acid aid cholesterol and fat absorption and reduce cholesterol disposal via bile acid synthesis.However, if including a cholate source is not desired for your research, diets without cholate are available.
| 研究用途 | 主要饮食特征 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| “西方”纯正致动脉粥样硬化饮食 | ||
| 加速高胆固醇血症和斑块形成的转基因模型,如APOE和Ldlr缺乏的小鼠。 用于饮食诱导肥胖的各种啮齿动物模型。 |
|
TD.88137 TD.10885 |
| 添加胆固醇和胆酸来源的“西方”纯动脉粥样硬化饮食* | ||
| 在野生型小鼠和大鼠中诱导高胆固醇血症和轻度动脉粥样硬化(泡沫细胞、脂肪条纹)。 不会助长肥胖。 |
|
TD.02028 TD.09237 |
| 添加胆固醇和胆酸盐的混合高脂饮食* | ||
| 在野生型小鼠和大鼠中诱导高胆固醇血症和轻度动脉粥样硬化(泡沫细胞、脂肪条纹)。 不会助长肥胖。 也用于造石(胆石)啮齿动物的研究。 |
|
TD.88051 TD.90221 |
| 添加胆固醇的标准饮食 | ||
| 在转基因和野生型模型中诱导高胆固醇血症而不促进肥胖。 |
|
TD.120097 TD.07841 TD.01383 |
*胆酸钠或胆酸有助胆固醇和脂肪的吸收,并可透过胆汁酸合成减少胆固醇的排出。然而,如果你的研究不想包括胆酸盐的来源,没有胆酸盐的饮食是可用的。
“Western” purified atherogenic diet
“Western” style diets are fed to genetically-modified cardiovascular models, such as Apoe and Ldlr deficient mice, to accelerate and enhance hypercholesterolemia and plaque formation and to elicit phenotypes commonly associated with metabolic syndrome.Within the atherogenic literature, a “Western” diet typically is described as a purified rodent diet with 20-23% milkfat/butterfat, 0.2% total cholesterol, and 34% sucrose by weight.TD.88137is an example of a “Western” style diet that was originally designed to characterize and enhance atherosclerosis development in a newly generated Apoe-deficient mouse model.Contact us for more information about “Western” style diets, modifications, or possible control diets.
Examples:
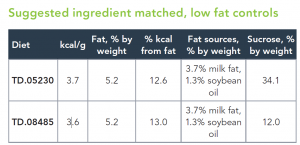
TD.88137Adjusted calories diet (42% from fat, 0.2% total cholesterol)
TD.1088545% fat Kcal diet (0.2% total cholesterol)
Research use:
Accelerated hypercholesterolemia and plaque formation in genetically-modified models, such as Apoe and Ldlr deficient mice.
Used for diet-induced obesity in a variety of rodent models.
Key dietary features:
High Fat Diet (20-23% by weight; 40 – 45% kcal from fat)
Saturated fatty acids (SFA >60% of total fatty acids)
Milkfat/butterfat
Sucrose (34% by weight)
Cholesterol (0.2% total)
References:
1.Febbraio, M., et al., Targeted disruption of the class B scavenger receptor CD36 protects against atherosclerotic lesion development in mice.J Clin Invest, 2000.105(8): p.1049-56.
2.Huszar, D., et al., Increased LDL cholesterol and atherosclerosis in LDL receptor-deficient mice with attenuated expression of scavenger receptor B1.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2000.20(4): p.1068-73.
3.Nakashima, Y., et al., ApoE-deficient mice develop lesions of all phases of atherosclerosis throughout the arterial tree.Arterioscler Thromb, 1994.14(1): p.133-40.
4.Nakashima, Y., et al., Upregulation of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 at atherosclerosis-prone sites on the endothelium in the ApoE-deficient mouse.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 1998.18(5): p.842-51.
5.Plump, A.S., et al., Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells.Cell, 1992.71(2): p.343-53.
6.Towler, D.A., et al., Diet-induced diabetes activates an osteogenic gene regulatory program in the aortas of low density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice.J Biol Chem, 1998.273(46): p.30427-34.
7,Tsuchiya, K., et al., FoxOs integrate pleiotropic actions of insulin in vascular endothelium to protect mice from atherosclerosis.Cell Metab, 2012.15(3): p.372-81.
“Western” purified atherogenic diet with added cholesterol and cholate source*
Wild type mice and rats generally are resistant to atherosclerosis, requiring more extreme dietary manipulation to modify lipoprotein profiles and develop mild atherosclerosis (foam cells, fatty streaks).Modern formulations are made completely of purified ingredients because this more refined approach has been reported to decrease the incidence of gallstones and liver damage associated with less refined and more traditional dietary approaches.To induce mild atherosclerosis in wild type animals, the “Western” purified diet can be modified to increase cholesterol (1-1.25%) and add a bile salt such as sodium cholate or cholic acid.Contact us for more information, modifications, or possible control diets.
Examples of purified high fat diets with added cholesterol and cholate source*:
TD.0202821% milkfat (1.25% cholesterol, 0.5% cholic acid)
TD.0923715% milkfat diet (1% cholesterol, 0.5% sodium cholate)
Examples of purified high fat diets with added cholesterol (without cholate source):
TD.9612121% milkfat (1.25% cholesterol)
Research Use:
Induce hypercholesterolemia and mild atherosclerosis (foam cells, fatty streaks) primarily in wild type mice and rats.
Will not promote obesity.
Key dietary features:
High fat diet (15-20% by weight; 34 – 45% kcal from fat)
Saturated fatty acids (SFA >55% of total fatty acids)
Milkfat/butterfat, cocoa butter
Sucrose (30-50% by weight)
Cholesterol (1 – 1.25%)
Cholate source (0.5%)*
References:
1.Bernal, C., et al., Lipid biomarkers and metabolic effects of lycopene from tomato juice on liver of rats with induced hepatic steatosis.J Nutr Biochem, 2013.24(11): p.1870-81.
2.Gao, Q., et al., Atherogenic diets exacerbate colitis in mice deficient in glutathione peroxidase.Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2010.16(12): p.2043-54.
3.Lichtman, A.H., et al., Hyperlipidemia and atherosclerotic lesion development in LDL receptor-deficient mice fed defined semipurified diets with and without cholate.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 1999.19(8): p.1938-44.
4.Marcondes, M.C., et al., Effects of chronic mental stress and atherogenic diet on the immune inflammatory environment in mouse aorta.Brain Behav Immun, 2011.25(8): p.1649-57.
5.Nishina, P.M., et al., Effects of dietary fats from animal and plant sources on diet-induced fatty streak lesions in C57BL/6J mice.J Lipid Res, 1993.34(8): p.1413-22.
6.Nishina, P.M., et al., Atherosclerosis and plasma and liver lipids in nine inbred strains of mice.Lipids, 1993.28(7): p.599-605.
7.Yue, P., et al., Enhanced hepatic apoA-I secretion and peripheral efflux of cholesterol and phospholipid in CD36 null mice.PLoS One, 2010.5(3): p.e9906.
8.Nishina, P.M., J. Verstuyft, and B. Paigen, Synthetic low and high fat diets for the study of atherosclerosis in the mouse.J Lipid Res, 1990.31(5): p.859-69.
*Sodium cholate or cholic acid aid cholesterol and fat absorption and reduce cholesterol disposal via bile acid synthesis.However, if including a cholate source is not desired for your research, diets without cholate are available.SeeTD.96121for a purified diet andTD.94059for a hybrid diet.Contact us for additional options.
Hybrid high fat diets with added cholesterol and cholate source*
Beverly Paigen and colleagues first characterized atherosclerosis development in C57BL/6 mice by feeding a hybrid atherogenic diet.The hybrid diet was created by mixing a natural ingredient mouse diet in a 3:1 ratio with a concentrated purified diet (containing 5% cholesterol and 2% sodium cholate; referred to as Thomas-Hartroft diet).The resulting mixture recreated inTD.88051/TD.90221(same formula) contains ~15.8% fat, 1.25% cholesterol, and 0.5% sodium cholate.This group later compared the hybrid atherogenic diet approach to the more modern “western” purified atherogenic diet with added cholesterol and cholate and found that the hybrid atherogenic diet induced more gallstones and liver damage.Hybrid diets contain a variety of unrefined ingredients that may modify lipid metabolism and atherogenesis and do not allow for precise control of ingredients and nutrients for the study of chronic diseases.Although more refined diets have been developed, hybrid atherogenic diets are still popular for inducing mild atherosclerosis and gallstones in wild type mice and rats.Contact us for more information, modifications, or possible control diets.
Examples of hybrid high-fat diets with added cholesterol and cholate source*:
TD.88051andTD.90221(same formula) are Teklad product codes for hybrid atherogenic diets
Example of hybrid high-fat diet with added cholesterol (without cholate source):
TD.94059
Research Use:
Induce hypercholesterolemia and mild atherosclerosis (foam cells, fatty streaks) primarily in wild type mice and rats.
Will not promote obesity.
Also used for lithogenic (gallstone) rodent studies.
Key dietary features:
75% rodent breeder diet; 25% purified ingredients
High fat (~15% by weight; 37% kcal from fat)
Saturated fatty acids (SFA >45% of total fatty acids)
Cholesterol (1.25%)
Cholate source (0.5%)*
References:
1.Nishina, P.M., J. Verstuyft, and B. Paigen, Synthetic low and high fat diets for the study of atherosclerosis in the mouse.J Lipid Res, 1990.31(5): p.859-69.
2.Clee, S.M., et al., Plasma and vessel wall lipoprotein lipase have different roles in atherosclerosis.J Lipid Res, 2000.41(4): p.521-31.
3.George, J., et al., Enhanced fatty streak formation in C57BL/6J mice by immunization with heat shock protein-65.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 1999.19(3): p.505-10.
4.Miyake, J.H., et al., Transgenic expression of cholesterol-7-alpha-hydroxylase prevents atherosclerosis in C57BL/6J mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2002.22(1): p.121-6.
5.Paigen, B., et al., Quantitative assessment of atherosclerotic lesions in mice.Atherosclerosis, 1987.68(3): p.231-40.
6.Schreyer, S.A., D.L. Wilson, and R.C. LeBoeuf, C57BL/6 mice fed high fat diets as models for diabetes-accelerated atherosclerosis.Atherosclerosis, 1998.136(1): p.17-24.
7.Vergnes, L., et al., Cholesterol and cholate components of an atherogenic diet induce distinct stages of hepatic inflammatory gene expression.J Biol Chem, 2003.278(44): p.42774-84.
*Sodium cholate or cholic acid aid cholesterol and fat absorption and reduce cholesterol disposal via bile acid synthesis.However, if including a cholate source is not desired for your research, diets without cholate are available.SeeTD.96121for a purified diet andTD.94059for a hybrid diet.Contact us for additional options.
Standard diets with added cholesterol
Standard, natural ingredient diets with cholesterol added are fed to induce hypercholesterolemia.Various levels of cholesterol, fat, and/or bile salts can be added to one of the numerous standard rodent diets stocked by Envigo Teklad.For many applications, adding these components to Envigo’s minimal-to-moderate phytoestrogen global rodent diets is recommended.Our minimal phytoestrogen global rodent diets are soybean meal free, limiting the effect of phytoestrogens on your research outcomes.Soybean meal, a common dietary source of phytoestrogens, has been shown to decrease aortic fatty streak development and modify plasma cholesterol, which may reduce the risk of developing atherosclerosis.Limiting dietary soybean meal may reduce confounding variables within your dietary-induced atherosclerosis model.Contact a nutritionist to discuss additional diet options.
Examples of minimal and moderate phytoestrogen rodent diets with added cholesterol:
TD.1200971% cholesterol diet (2020 – minimal phytoestrogens)
TD.078412% cholesterol diet (2016 – minimal phytoestrogens)
TD.013832% cholesterol (2018 – Moderate phytoestrogens)
Research use:
Induce hypercholesterolemia in genetically-modified and wild type models without promoting obesity.
Key dietary features:
Standard, grain-based rodent diet
Minimal/moderate phytoestrogen diets recommended
Cholesterol (1 – 4%)
References:
1.Belch, J.J., et al., Longitudinal assessment of endothelial function in the microvasculature of mice in-vivo.Microvasc Res, 2013.85: p.86-92.
2.Hartvigsen, K., et al., A diet-induced hypercholesterolemic murine model to study atherogenesis without obesity and metabolic syndrome.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2007.27(4): p.878-85.
Diets for additional animal models of atherosclerosis
Rabbits, hamsters, and swine are common models of atherosclerosis.Contact a nutritionist for information and formula examples.Seerabbit, swine and other speciesfor information and formula examples.
“西方”纯正致动脉粥样硬化饮食
例子:
- TD.88137调整卡路里饮食(42%来自脂肪,0.2%总胆固醇)
- TD.1088545%脂肪KCAL饮食(总胆固醇0.2%)
研究用途:
加速高胆固醇血症和斑块形成的转基因模型,如APOE和Ldlr缺乏的小鼠。
用于饮食诱导肥胖的各种啮齿动物模型。
主要饮食特征:
- 高脂肪饮食(按体重计算占20-23%;脂肪占40-45%)
- 饱和脂肪酸(SFA>总脂肪酸的60%)
- 乳脂/乳脂
- 蔗糖(按重量计占34%)
- 胆固醇(总数0.2%)
添加胆固醇和胆酸来源的“西方”纯动脉粥样硬化饮食*
添加胆固醇和胆酸盐来源的纯化高脂饮食的例子*:
- TD.0202821%乳脂(1.25%胆固醇,0.5%胆酸)
- TD.0923715%乳脂饮食(1%胆固醇,0.5%胆酸钠)
添加胆固醇的纯化高脂饮食的例子(没有胆酸来源):
- TD.9612121%乳脂(1.25%胆固醇)
研究用途:
主要在野生型小鼠和大鼠诱发高胆固醇血症和轻度动脉粥样硬化(泡沫细胞、脂肪条纹)。
不会助长肥胖。
主要饮食特征:
- 高脂饮食(体重15-20%;脂肪34-45千卡)
- 饱和脂肪酸(SFA>总脂肪酸的55%)
- 乳脂/黄油、可可脂
- 蔗糖(重量占30%-50%)
- 胆固醇(1-1.25%)
- 巧克力源(0.5%)*
*胆酸钠或胆酸有助胆固醇和脂肪的吸收,并可透过胆汁酸合成减少胆固醇的排出。然而,如果你的研究不想包括胆酸盐的来源,没有胆酸盐的饮食是可用的。看见TD.96121为了纯正的饮食TD.94059混合饮食。请与我们联系,了解其他选项。
添加胆固醇和胆酸盐的混合高脂饮食*
添加胆固醇和胆酸盐的混合高脂饮食实例*:
- TD.88051和TD.90221(相同的配方)是特克拉德混合动脉粥样硬化饮食的产品代码。
添加胆固醇的混合高脂饮食的例子(没有胆酸来源):
- TD.94059
研究用途:
主要在野生型小鼠和大鼠诱发高胆固醇血症和轻度动脉粥样硬化(泡沫细胞、脂肪条纹)。
不会助长肥胖。
也用于造石(胆石)啮齿动物的研究。
主要饮食特征:
- 75%的啮齿动物饲养员;25%的纯化成分
- 高脂肪(体重约15%;脂肪37%千卡)
- 饱和脂肪酸(SFA>总脂肪酸的45%)
- 胆固醇(1.25%)
- 巧克力源(0.5%)*
*胆酸钠或胆酸有助胆固醇和脂肪的吸收,并可透过胆汁酸合成减少胆固醇的排出。然而,如果你的研究不想包括胆酸盐的来源,没有胆酸盐的饮食是可用的。看见TD.96121为了纯正的饮食TD.94059混合饮食。请与我们联系,了解其他选项。
添加胆固醇的标准饮食
添加胆固醇的最小和中度植物雌激素啮齿动物饮食的例子:
- TD.120097 1%胆固醇饮食(2020年-最小植物雌激素)
- TD.07841 2%胆固醇饮食(2016年-最小植物雌激素)
- TD.01383 2%胆固醇(2018年-中度植物雌激素)
研究用途:
在转基因和野生型模型中诱导高胆固醇血症而不促进肥胖。
主要饮食特征:
- 标准的、以谷物为基础的啮齿动物饮食
- 最小/中度植物雌激素饮食建议
- 胆固醇(1-4%)