BioXcell热销产品–InVivoPlus anti-mouse PD-1 (CD279)
BioXcell热销产品–InVivoPlus anti-mouse PD-1 (CD279)
产品描述:
BioXcell InVivoPlus anti-mouse PD-1 RMP1-14单克隆抗体与小鼠PD-1(也称为CD279)反应。PD-1是一种50-55kDa的细胞表面受体,由Pdcd1基因编码,属于Ig超家族的CD28家族。PD-1在CD4和CD8胸腺细胞以及活化的T和B淋巴细胞和髓细胞上瞬时表达,在成功消除抗原后PD-1的表达下降。此外,在B细胞前阶段,Pdcd1 mRNA在发育中的B淋巴细胞中表达。PD-1的结构包括ITIM(基于免疫受体酪氨酸的抑制基序),这表明PD-1负调控TCR信号。PD-1通过结合B7家族的成员PD-L1和PD-L2发出信号。在配体结合后,PD-1信号传导抑制T细胞活化,导致增殖减少,细胞因子产生和T细胞死亡。此外,PD-1敲除动物表现出扩张型心肌病、脾肿大和外周耐受丧失,在小鼠的外周耐受性和预防自身免疫性疾病中发挥关键作用。诱导的PD-L1表达常见于许多肿瘤,包括鳞状细胞癌、结肠癌和乳腺癌。PD-L1过度表达会导致肿瘤细胞对CD8T细胞介导的裂解的抗性增加。在黑素瘤的小鼠模型中,可以通过用阻断PD-L1与其受体PD-1之间相互作用的抗体治疗来暂时抑制肿瘤生长。由于这些原因,目前正在探索抗PD-1介导的免疫疗法作为癌症治疗。与J43抗体一样,RMP1-14抗体已显示阻断小鼠PD-L1-Ig和小鼠PD-L2-Ig与PD-1的结合。
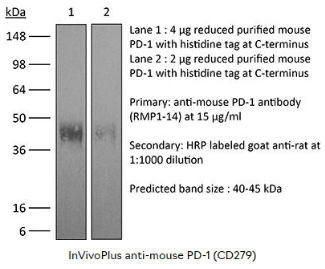
产品详情:
|
产品名称 |
InVivoPlus anti-mouse PD-1 (CD279) |
|
产品货号 |
BP0146 |
|
产品规格 |
5/25/50/100mg |
|
反应种属 |
Mouse |
|
克隆号 |
RMP1-14 |
|
同种型 |
Rat IgG2a, κ |
|
免疫原 |
Syrian Hamster BKH cells transfected with mouse PD-1 cDNA |
|
实验应用 |
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling |
|
产品形式 |
PBS, pH 7.0,Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
|
纯度 |
>95%, Determined by SDS-PAGE |
|
聚合 |
<5%, Determined by SEC |
|
无菌处理 |
0.2 µm filtration |
|
纯化方式 |
Protein G |
|
RRID |
AB_10949053 |
|
分子量 |
150 kDa |
|
小鼠病原检测 |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
|
保存条件 |
抗体原液保存在4°C,不能冷冻保存。 |
|
推荐同型对照 |
InVivoPlus rat IgG2a isotype control, anti-trinitrophenol(货号BP0089) |
|
推荐抗体稀释液 |
InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer(货号IP0070) |
为什么选择InVivoPlus抗体?
InVivoPlus级别的产品内毒素含量更低,经过多种实验验证,更适合用于体内实验研究
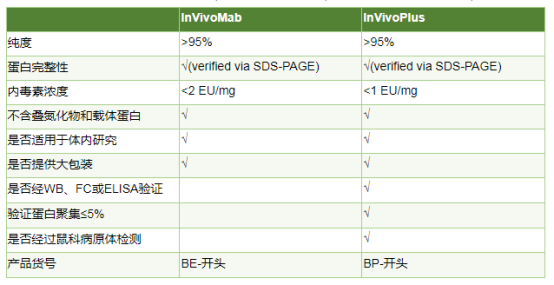
该产品自上市已被多篇SCI文献引用,品质有保证,以下是部分已发表的文献引用:
|
应用 |
文章 |
|
体内PD-1/PD-L信号阻断 (in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling) |
1. Triplett, T. A., et al. (2018). ‘Reversal of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated cancer immune suppression by systemic kynurenine depletion with a therapeutic enzyme’ Nat Biotechnol 36(8): 758-764. 2. Grasselly, C., et al. (2018). ‘The Antitumor Activity of Combinations of Cytotoxic Chemotherapy and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Is Model-Dependent’ Front Immunol 9: 2100. 3. Moynihan, K. D., et al. (2016). ‘Eradication of large established tumors in mice by combination immunotherapy that engages innate and adaptive immune responses’ Nat Med. doi : 10.1038/nm.4200. 4. Ngiow, S. F., et al. (2015). ‘A Threshold Level of Intratumor CD8+ T-cell PD1 Expression Dictates Therapeutic Response to Anti-PD1’ Cancer Res 75(18): 3800-3811. 5. Evans, E. E., et al. (2015). ‘Antibody Blockade of Semaphorin 4D Promotes Immune Infiltration into Tumor and Enhances Response to Other Immunomodulatory Therapies’ Cancer Immunol Res 3(6): 689-701. 6. Zelenay, S., et al. (2015). ‘Cyclooxygenase-Dependent Tumor Growth through Evasion of Immunity’ Cell 162(6): 1257-1270. 7. Zander, R. A., et al. (2015). ‘PD-1 Co-inhibitory and OX40 Co-stimulatory Crosstalk Regulates Helper T Cell Differentiation and Anti-Plasmodium Humoral Immunity’ Cell Host Microbe 17(5): 628-641. |
更多产品详情请咨询 BioXcell 中国代理——上海金畔生物
